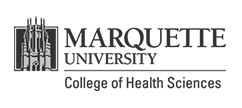Spine
Anatomy
Cervical Spine Anatomy
The knee joint is formed by the union of two bones, namely the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (lower leg bone). At the junction of these two bones is a cartilage called the meniscus, which acts as a shock absorber. There are two menisci – the lateral and medial menisci. The lateral meniscus is the outer meniscus of the knee joint and gives a cushioning effect during weight bearing activities. Lateral meniscus syndrome is characterised by an injury caused by the tearing of the cartilage tissue or a rare case of a congenital abnormality called a discoid meniscus, which results in knee pain.
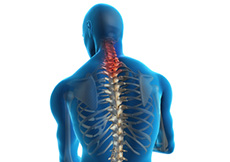
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
Thoracic spine is the central part of the spine, also called as dorsal spine, which runs from the base of the neck to the bottom of your rib cage. The thoracic spine provides flexibility that holds the body upright and protects the organs of the chest.
Spine is made up of 24 spinal bones, called as vertebra, of which, the thoracic region of the spine is made up of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12).
Lumbar Spine Anatomy
The spine, also called the back bone, plays a vital role in stability, smooth movement and protection of the delicate spinal cord. It is made up of bony segments called vertebra with fibrous tissue called intervertebral discs between them. The vertebra and discs form the spinal column from the head to the pelvis, giving symmetry and support to the body.
Conditions
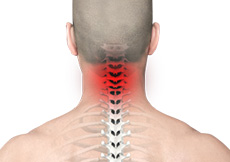
Neck Pain
The first 7 vertebral bones on the spinal column form the cervical spine and are in the neck region. The neck bears the weight of the head, allows significant amount of movement, and less protected than other parts of spine. All these factors make the neck more susceptible to injury or other painful disorders. Common neck pain may occur from muscle strain or tension in everyday activities including poor posture, prolonged use of a computer and sleeping in an uncomfortable position.
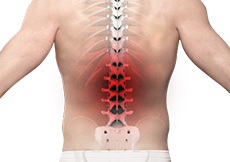
Back Pain
Back pain or backache is the pain felt in the back that may originate from muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine. Back pain is one of the most common medical problems experienced by most people at some time in their life. Back pain can be acute usually lasting from few days to few weeks, or chronic lasting for more than three months.
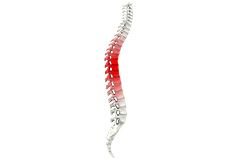
Spine Trauma
Spine trauma is damage to the spine caused from a sudden traumatic injury caused by an accidental fall or any other physical injury. Spinal injuries may occur while playing, performing normal activities, operating heavy machines, lifting heavy objects, driving automobiles, or when you suffer a fall. Injury to spine may cause various conditions including fractures, dislocation, partial misalignment (subluxation), disc compression (herniated disc), hematoma (accumulation of blood) and partial or complete tears of ligaments.
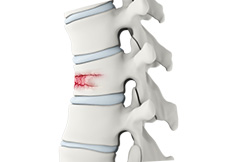
Vertebral Compression Fractures
Back pain is an indication of stress fractures known as vertebral compression fractures. Vertebral compression fractures occur when the normal vertebral body of the spine is squeezed or compressed to a smaller height. The bone collapses when too much pressure is placed on the vertebrae, resulting in pain, limited mobility, height loss, and spinal deformity.
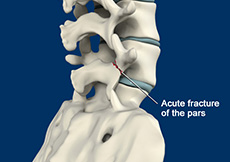
Spondylolysis
Spondylolysis is a stress fracture of vertebra that may progress into spondylolisthesis, a condition of displacement of vertebrae from the spinal column. Spondylolysis is the cause for frequent low back pain in children. It is more common among children and teenagers who participate actively in sports such as football, weightlifting and gymnastics.
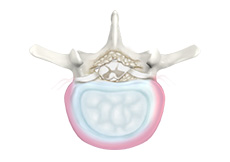
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) refers to gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. DDD is a misnomer as it is not actually a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to advancing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics. DDD is commonly seen in individuals over 50 years of age.
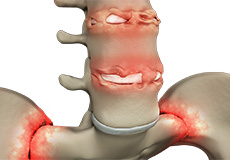
Ankylosing Spondylitis
The term ankylosis stands for loss of mobility of the spine, whereas spondylitis means inflammation of the spine. Therefore, ankylosing spondylitis is a condition where chronic inflammation of spine and sacroiliac joint, results in complete fusion of the vertebrae leading to pain and stiffness in the spine. Sacroiliac joints are present in the lower back where the sacrum part of the vertebrae joins the iliac bones.
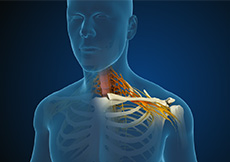
Cervical Radiculopathy/Myelopathy
The spine, also called the back bone, is designed to give us stability, smooth movement, as well as providing a corridor of protection for the delicate spinal cord. It is made up of bony segments called vertebrae and fibrous tissue called intervertebral discs. Disc protrusion, also called herniated disc, is a condition caused by a tear in an intervertebral disc allowing the disc contents to bulge out.
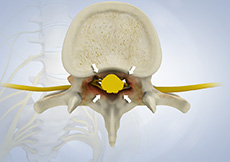
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition caused from the vertebral column constricting and exerting pressure on the spinal cord or neural foramen (a bony tunnel through which a nerve exits the spinal cord).
Spinal Stenosis usually affects the cervical and lumbar spine. If the spinal canal is narrowed, the disorder is called cervical/lumbar central stenosis.
Procedures
Non-Surgical Procedures
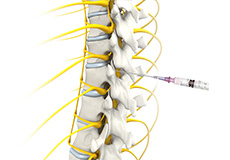
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural spinal injection is a non-surgical treatment option utilized for relieving back pain. Spine degenerative conditions such as herniated disc, spinal stenosis and many others may induce back pain due to the compression of the associated spinal nerves. This pain or numbness may extend to the other parts of the body such as hips, buttocks, and legs. Doctors start with non-surgical methods to treat back pain and epidural spinal injection is one of these preferences.
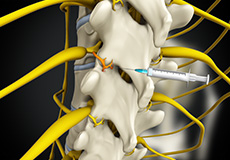
Medial Branch Block Injections
Medical branch block is an injection of a local anesthetic near the medial branch nerves to temporarily block the pain signal carried from the facet joints of the spine to the brain. It is used to assist your physician in diagnosing the cause of your back pain.
Surgical Procedures
Vertebroplasty
Osteoporosis is a “silent” disease characterized by weakening of bones, making them more susceptible to fractures, typically in the hip and spine. Elderly people and especially post-menopausal women are at greater risk of developing osteoporosis.
Spine Deformity Surgery
The Spine or backbone provides stability to the upper part of our body. It helps to hold the body upright. It consists of several irregularly shaped bones, called vertebrae appearing in a straight line. The spine has two gentle curves, when looked from the side and appears to be straight when viewed from the front.

Robotic Spine Surgery
Robotic Assisted Spine Surgery is a minimally invasive spine surgery where the surgeon is assisted by a robotic system (Da Vinci surgical system) to perform the surgery. Robotic systems are becoming increasingly popular in the medical fraternity owing to the unique advantages including the precision, safety and many other advantages.
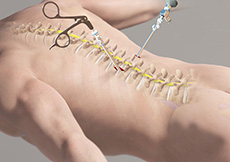
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
MISS is the latest advanced technology available to perform spinal surgeries through small, less than one inch long, incisions. It involves the use of special surgical instruments, devices and advanced imaging techniques to visualize and perform the surgery through such small incisions. MISS is aimed at minimizing damage to the muscles and surrounding structures.
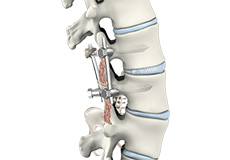
Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion is the surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae. Fusion of the vertebrae involves insertion of secondary bone tissue obtained either through auto graft (tissues from the same patient) or allograft (tissues from the other person) to augment the bone healing process.